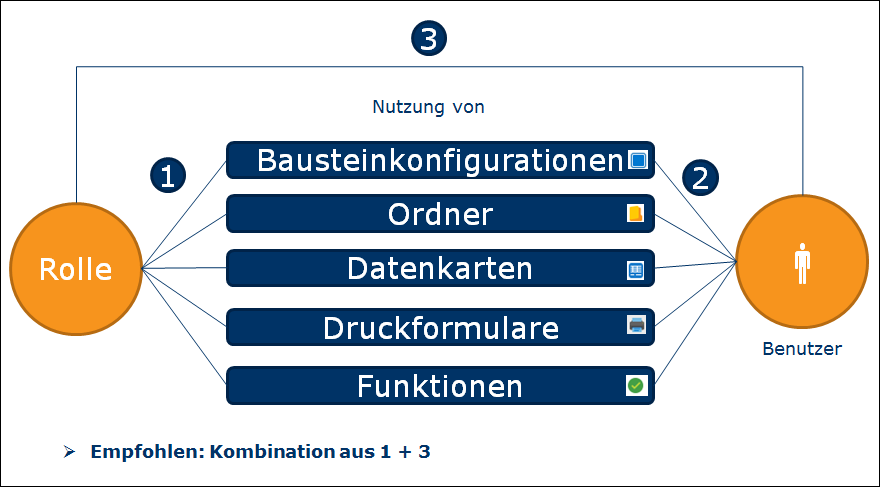
TiCon offers a sophisticated authorization concept. It is possible to assign rights to the role (1), directly to the user (2), or to the user via a role (3).
Rights can be assigned to a Benutzer or Rolle for the following categories:
•![]() Element configurations
Element configurations
•![]() Folder
Folder
•![]() Data cards
Data cards
•![]() Print forms
Print forms
Note: |
There is no hierarchy for permissions, i.e. there is no role or user with a parent function. Folder rights have a special logic and correspond to Windows' logic. |
![]() Configuration options
Configuration options
•Standard = Not authorized --> The permission has to be assigned intentionally. •Permission levels for: –Admin functions, folders, element configurations, data cards, print forms: > Read > Read/Write > Locked –Functions (except for the module functions): > Activated > Locked –Module functions: > Full license > Read-only license If the authorization "Standard (Not authorized)" has been assigned, then the role does not include or the user does not have the specific permissions. However, the user might receive the same permission from another role.  |
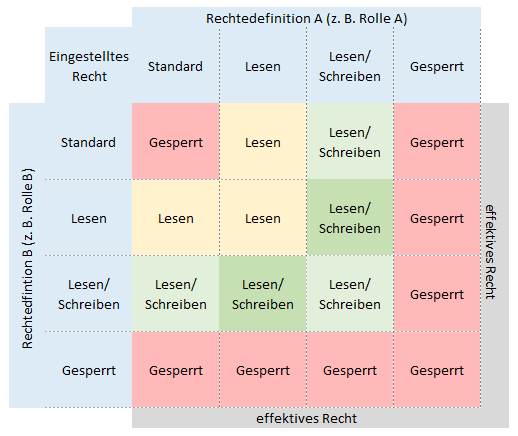
The following table shows the effective authorization, if permissions have been defined at more than one place. All places for permissions are treated equally.
The definition of permissions can be the setting at a role, user, element configuration, data card etc.
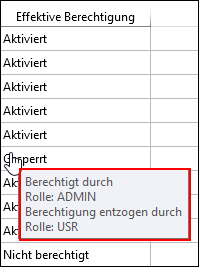
For roles / users, there is a tooltip for the column “Effective authorization”, which shows by which role a permission has been set or revoked. As soon as the permission of a role has been set to “Locked”, this function is “Locked” – regardless of whether another role has another authorization.
|
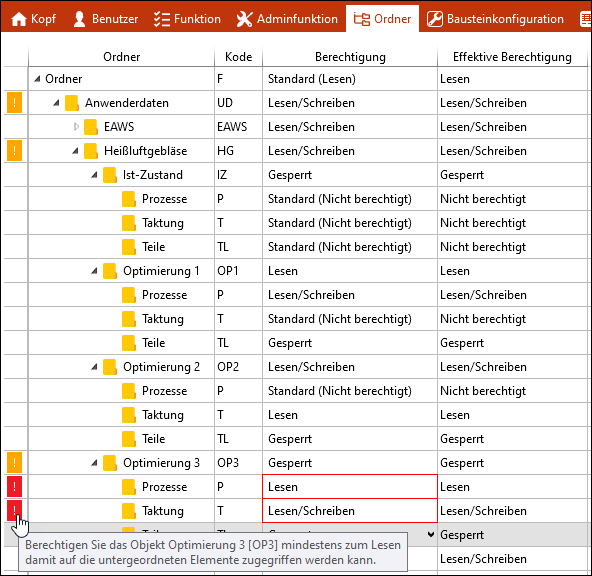
![]() Meaning of permissions on folders
Meaning of permissions on folders
Permissions on folders only apply to this folder, not to its subfolders. "Read" is the minimum permission required to view a subfolder. •Example 1: The "Actual state" folder has the "Locked" permission: This means that its subfolders are "Locked" as well and cannot be accessed. The authorization must be set to "Standard (Not authorized)". •Example 2: Folder "Optimization 1" has the "Read" permission: This means that its subfolders can be accessed as well and can be given specific permissions. •Example 3: Folder "Optimization 2" has the "Read/write" permission: This means that its subfolders can be accessed as well and can be given specific permissions. •Example 4: Folder "Optimization 3" has the "Locked" permission, the subfolders have distinct permissions. This constellation prevents saving. A corresponding warning message assists with the correction of the settings.
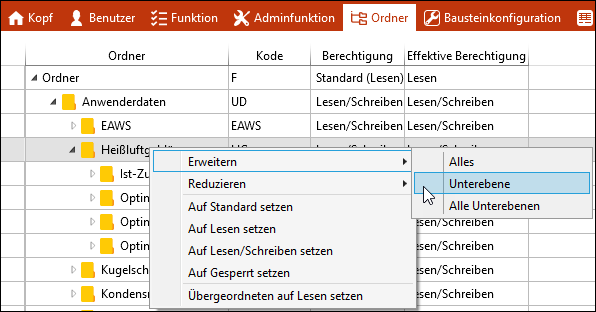
For setting the folder permissions you can also use the context menu.
Context menu for folder permissions If there is a conflict concerning the permissions in a subfolder, for all parent folders a warning will be displayed. |
![]() Rights in the Element configurations tab
Rights in the Element configurations tab
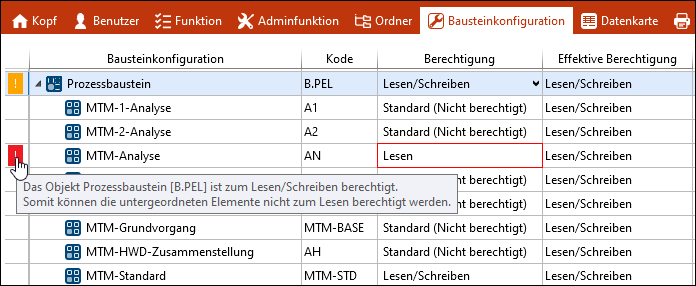
Observe the following when setting the permissions for element configurations. In general, the authorization is as described under effektivem Recht. In the following, the behavior is described using two examples. 1. Constellation cannot be saved Element type process element = Read/Write All element configurations, the standard (Not authorized) = Read/Write MTM standard [MTM-STD] = Read/Write MTM analysis [AN] = Read
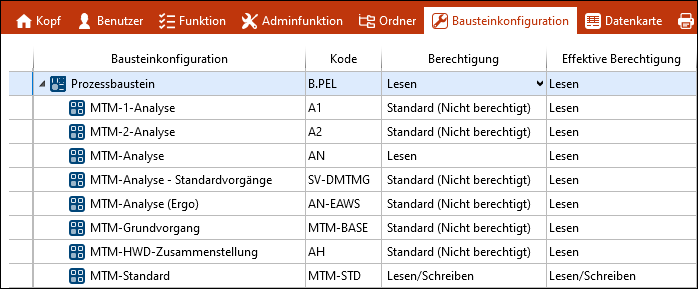
2. Correctly set permissions Element type process element = Read All element configurations, the standard (Not authorized) = Read MTM standard [MTM-STD] = Read/Write
|