The number of possible workplaces is required as input for the evaluation, as well as the selection of the relevant rotation plan (fair distribution, even distribution, uneven distribution) according to which the evaluation should be carried out.
Note: |
When examining the job rotation, an average working time of 7–8 hours is assumed. If the shift duration deviates from this time, the job rotation can still be used to determine an ergonomically advantageous job rotation. |
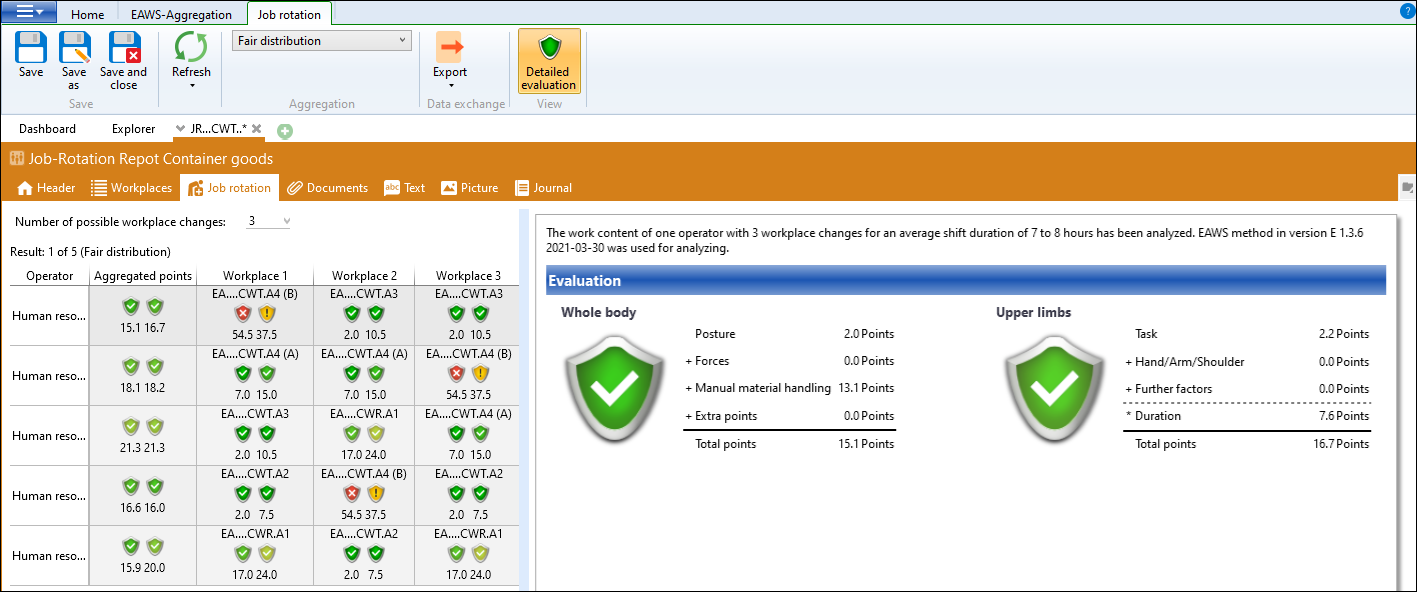
Tab Job rotation
The result should be interpreted as follows:
The first operator works the first third of their shift at workplace EA....CWT.A4 (B) and then changes to workplace EA....CWT.A3. They then remain the last third party at this workplace. The second operator starts at workplace EA....CWT.A4 (A) etc. Each operator changes their workplace no more than twice, which means they work at a maximum of 3 workplaces. This ensures that all operators are "green" despite a "red" workplace. For example, operator 1 is assessed with 15.1 points for the entire body and 17.3 points for the upper limbs despite working at an EA....CWT.A4 (B) workplace. If they worked there for the entire duration of the shift, they would be assessed with a red rating of 54.5 points for the entire body and 37.5 points for the upper limbs.
Procedure:
1. Add workplaces in "Workplaces" tab
2. Select the number of possible workplace changes (1–10) in "Job rotation" tab
Note: |
The number of workplace changes indicates how often operators change workstations. It is assumed that the operators work the same amount of time at each workplace. With a number of 1, one change takes place so that a worker works at one workplace for the first half of the shift and then moves to a different one if required. |
3. Click on "Refresh" / "Job rotation"
4. Change between the different aggregations via the "Job rotation" ribbon / "Aggregation" and select the most suitable change system for the particular situation.
Selection of aggregation
Note: |
Clicking "Refresh" / "Job rotation" calculates several rotation plans. The rotation of an operator is displayed in one row of the rotation plan. The aggregated EAWS® evaluation ("Aggregated points" column) for this rotation is independent of the sequence in which the workplace changes. The determined rotation plan for all operators fulfills the condition that each workplace can only be staffed by one operator at a certain point in time within the rotation plan. Alternatively, the Aggregation can be used to specify a certain rotation of workplaces. |
The rotation duration is constant. It is calculated as follows: Net shift time / (number of workplace changes +1).
Depending on the points from Sections 1–3 and Section 4 of the workplaces, possible aggregations of results are created. Strains from Sections 1–4 (body posture, forces, load handling, and strains on the upper limbs) are spread evenly across operators.
The job rotations are calculated using the "Refresh" button. The "Detailed evaluation" button shows the composition of the aggregated points. The evaluation of the individual workplaces is displayed on the workplace name with a tooltip.
The result of an aggregation can be exported using the "Job rotation" ribbon / "Data exchange" / "Export".
The following options are available:
•Job rotation as picture
•Job rotation as picture to clipboard
•Job rotation as text to clipboard
Data copied to the clipboard can then be inserted in Excel for further processing.
The following rotation plans are calculated:
•Fair distribution – the workplaces are distributed in such a way that the workload is evenly distributed among all operators. This distribution is displayed first.
•Equal distribution – every operator should work once at every workplace. It is ideal if the number of workplaces and the change of workplaces fit together perfectly.
•Uneven distributions - The workplaces are distributed in such a way that the workload on all workers is as low as possible.
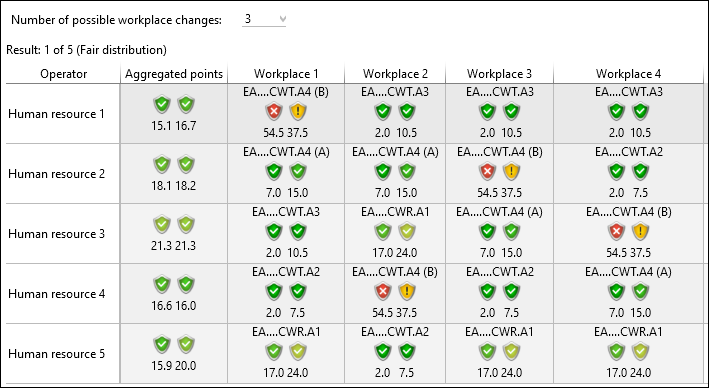
Fair distribution
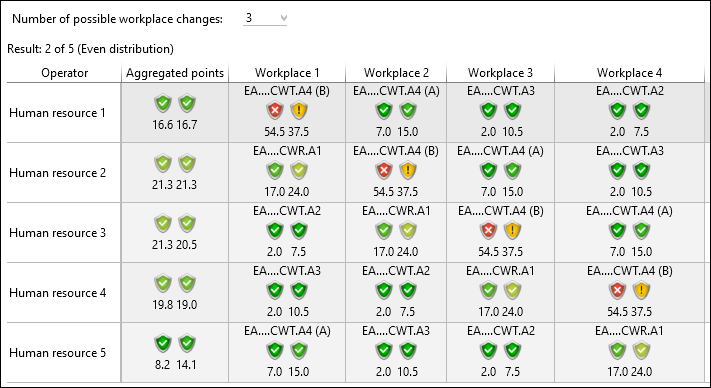
Even distribution
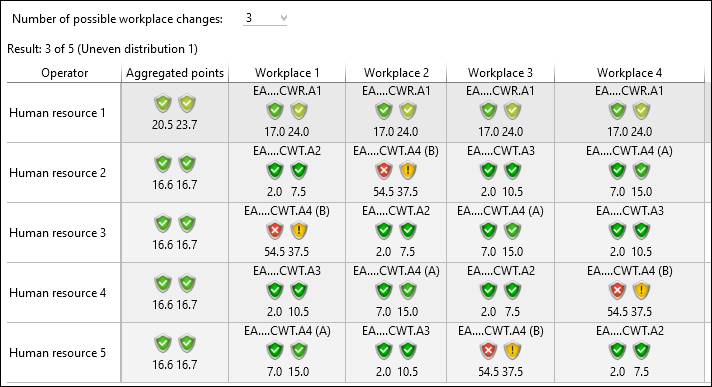
Uneven distribution